temni sadeži vir življenja
Flavin7 - Stemxcell - Cardio Flavin - Cyto Flavin
Avemar - Nano Silver - Koloidno srebro
Orogranule Pachira
Čez 5 sekund boste preusmerjeni na novo spletno stran: www.avemar-rak.com

Natural
Where does Avemar come
from?
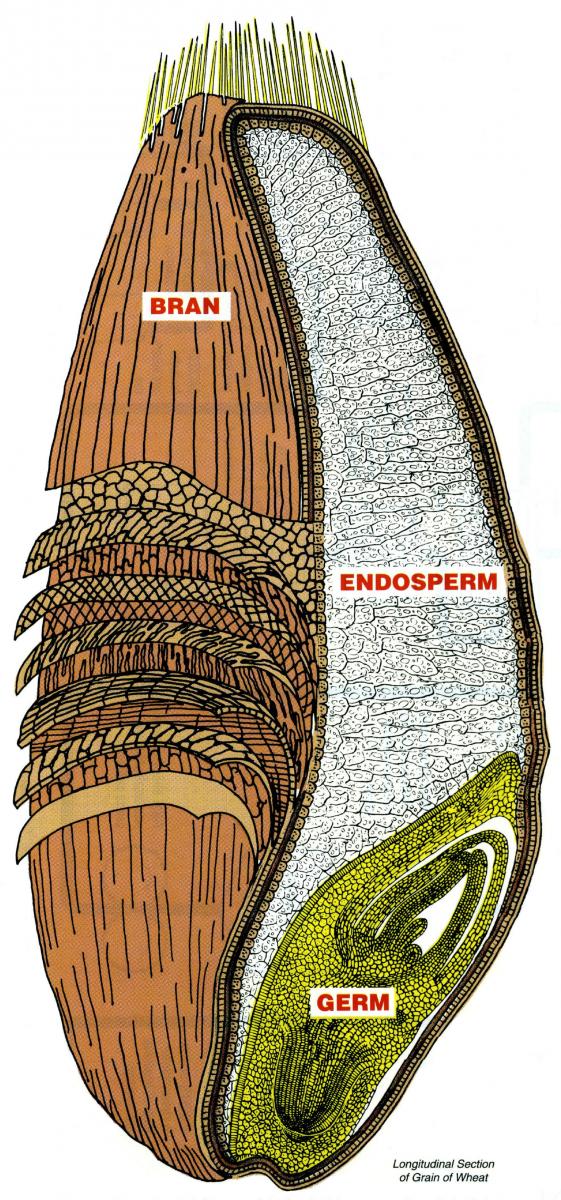 The
wheat grain kernel consists of 3 parts. The endosperm is the embryo of
the kernel. It makes up 83% of the kernel and is the source of energy
for new wheat plants if the kernel is planted and sprouts. It is high
in starch and gluten (the protein in wheat flour),but relatively low in
vitamin and mineral content. The endospermis used to make white flour.
The bran (14%) consists of the thin outer layers of the wheat kernel
and contains vitamins, minerals,and fiber. The germ makes up only 2%-3%
of the wheat kernel and is the most nutritious part of the wheat
kernel. Nutrients are concentrated in the germ, and it is rich in
vitamins, minerals, proteins, and fats. Wheat germ contains high levels
of tocopherol and B vitamins. It is separated from the other wheat
components by the milling process. Whole-wheat flours are made by
milling the whole kernel; that is, all 3 of the above parts of the
wheat kernel.
The
wheat grain kernel consists of 3 parts. The endosperm is the embryo of
the kernel. It makes up 83% of the kernel and is the source of energy
for new wheat plants if the kernel is planted and sprouts. It is high
in starch and gluten (the protein in wheat flour),but relatively low in
vitamin and mineral content. The endospermis used to make white flour.
The bran (14%) consists of the thin outer layers of the wheat kernel
and contains vitamins, minerals,and fiber. The germ makes up only 2%-3%
of the wheat kernel and is the most nutritious part of the wheat
kernel. Nutrients are concentrated in the germ, and it is rich in
vitamins, minerals, proteins, and fats. Wheat germ contains high levels
of tocopherol and B vitamins. It is separated from the other wheat
components by the milling process. Whole-wheat flours are made by
milling the whole kernel; that is, all 3 of the above parts of the
wheat kernel.
Non-toxic
The primary basis on which the safety of Avemar pulvis is established is that it consists primarily of fermented wheat germ with the added drying aids maltodextrin and silicon dioxide. Wheat germ, both fermented and unfermented, has been a part of the human diet for millennia with no indication that it poses any health hazards. The fermented wheat germ inAvemar pulvis is substantially equivalent to the fermented wheat germ found in whole-wheat foods and it is likely that many individuals have daily intakes of wheat germ in excess of 10 g from consumption of whole wheat products. Thus, historically safe consumption of whole-wheat products provides strong evidence of the safety of Avemar pulvis for its intended use.
In addition to a history of safe use of wheat germ, the safety of Avemar pulvis has been evaluated in acute, subacute, subchronic, and genetic toxicity studies and found to have no adverse effects at exposures far in excess of those that are expected to result from its intended use. In experimental animals, Avemar pulvis has been administered at high oral doses (commonly 3 g/kg bw/day and up to 5 g/kg bw/day) for extended periods of time without any evidence of toxicity. Data from clinical studies, often with humans in late-stage disease states and having weakened resistance, using dose levels (8.5 g/day) similar to those resulting from the intended use of Avemar pulvis, further demonstrate its safety over extended periods of time. Indeed, in several instances, supplementation with Avemar pulvis appeared to lessen the side effects of drug therapy.
The available data support the conclusion that the intake of Avemar pulvis would not be expected to cause adverse effects in humans under the conditions of its intended use as an ingredient in dietary supplements to be taken at recommended doses for extended periods of time.
J. T. et al (2007): Safety studies regarding a standardized extract of Fermented wheat germ.
Safe
Several studies have been carried out to evaluate the safety of Avemar in doses used for treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases.
Boros et al discussed some of the studies in animals and humans that provide an indication of its safety; studies in these species to date suggest few adverse effects of Avemar. Acute and subacute toxicology tests carried out in a Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) setting revealed minimal side effects. Toxicity studies in the rat and mouse demonstrated an acute oral LD50 of Avemar in male and female mice and rats of greater than 2,000 mg/kg. The no-observable adverse effect level, which is the greatest concentration or amount of Avemar that causes no detectable adverse alteration, was 2,000 mg/kg/day in rats, and in a subchronic study with mice and rats was found to be 3,000 mg/kg/day. There is a wide therapeutic window for Avemar. Doses toxic to normal cells are more than 50 times higher than the dosage recommended for therapy, which suggests that a wide range of therapeutic dosages can be tested before the product becomes toxic.
The US Food and Drug Administration recently granted Avemar a status of Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS), which allows it to be used in foods, drinks, and dietary supplements. Significant side effects have not been reported, but mild and transient diarrhea, nausea, flatulence, soft stool, constipation, dizziness, and increase in body weight can accompany the consumption of Avemar. Hematologic evaluations of hospitalized cancer patients in Hungary found that the white blood cell count, lymphocyte count, neutrophil granulocyte count, monocyte count, eosinophil granulocyte count, hemoglobin level, red blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hematocrit, platelet count, and prothrombin level were normal after 1-5 years of Avemar treatment.
Molecular targets
MHC-1 (Major Histo-compatibility Class 1 protein)
Tumors can fool the immune system by disguising themselves as normal cells. They can develop a camouflage by expressing high levels of MHC-I in order to to avoid recognition by the specific cells of the immune system that play an important role in antitumor defense – the so called natural killer (NK) cells. Natural killer cells recognize and are blocked by the expression of MHC-I molecules on their target cells. As Avemar reduces the MHC-I level on human tumor cells, it sensitizes them against NK killing, thus reducing their metastatic activities.
ICAM-1 (Intercellular adhesion molecule-1)
In order to defend the body effectively, some cells of the immune system – the leucocytes – require special molecules to help them get through the walls of the vessels and infiltrate the attacker. One of these special molecules is called the ICAM-1. In the presence of abundant amounts of ICAM-1, leukocytes can get through the walls of the vessels easily. It is known that the inner cells of the vessels of some tumors have smaller amount of ICAM-1 compared to normal cells, and this phenomenon can be considered an escape mechanism because efficient leukocyte infiltration is impaired. It has been shown that Avemar makes more ICAM-1 on the cells of the vessels, thus helping the leucocytes to infiltrate the tumor.
RR (ribonucleotid reductase)
Ribonucleotide reductase (RR) is an enzyme, and is needed for DNA synthesis. It was demonstrated that this enzyme is more active in cancer cells, and therefore looks like excellent target for cancer chemotherapy. It was shown that Avemar blocks this enzyme, which favorably impairs the creation of DNA for cancer cells.
PARP (Poly-ADP–ribose-Polymerase)
PARP is an enzyme that plays a pivotal role in repairing the DNA chains. The activity of this enzyme is extremely high in cancer cells because they are highly dependent upon the active function of their DNA. In the presence of PARP, the cells can correct their eventual mistakes, which coincidentally happen during cell division. Similarly, if PARP does not work well, it leads to DNA fragmentation and thus to cell death (called apoptosis). Avemar inhibits PARP, therefore DNA repair in cancer cells is also impaired. It was also shown that Aveamar does not trigger apoptosis in healthy cells.
COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes
These enzymes play a crucial role in the immune system, and the pharmacological inhibition of COX can provide relief from the symptoms of inflammation and pain. Avemar non-selectively inhibits both of these enzymes and this feature may partly explain its anti-inflammatory activities against adjuvant arthritis in rats and rheumatoid arthritis in humans.
Tuji članki

- 30 PubMed publications - povezava na spletno stran PubMed, kjer je objavljenih 30 publikacij vezanih na izdelek Avemar.
- Health Science Institute - Članek
objavljen Decembra 2005

- Alternatives
for the health conscious individual

- Anti-Angin Medical News - Članek
objavljen 2008

